
- #DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT CODE#
- #DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT PROFESSIONAL#
- #DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT WINDOWS#
#DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT WINDOWS#
Mirrored volumes or RAID-5 volumes cannot be created on Windows XP Professional-based computers. With dynamic storage, disk and volume management can be performed without the need to restart Windows. A dynamic disk contains dynamic volumes, such as simple volumes, spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID-5 volumes. Dynamic disk storageĪ disk initialized for dynamic storage is called a dynamic disk. Windows XP does not support this multidisk basic volume. Additionally, basic volumes include multidisk volumes, which are created by using Windows NT 4.0 or earlier, such as volume sets, stripe sets, mirror sets, and stripe sets with parity. A basic disk contains basic volumes, such as primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives. Basic disk storageĪ disk initialized for basic storage is called a basic disk. Microsoft Windows XP offers two types of disk storage: basic and dynamic.
#DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT PROFESSIONAL#
Windows XP Professional is designed to allow multiple applications to run simultaneously, while ensuring great system response and stability.
#DISK FORMATTING WHY ARE CLUSTER SIZES IMPORTANT CODE#
Windows XP Professional is built on the proven code base of Windows NT and Windows 2000, which features a 32-bit computing architecture, as well as a fully protected memory model. Michel, in Computer Systems Performance Evaluation and Prediction, 2003 13.2.2 Windows XP architecture When you use / f:Size to define the size of the disk, you cannot use the /t:Tracks or /n:Sectors parameter. Microsoft recommends that you use the / f:Size parameter instead of using these two parameters together. Used together to specify the number of tracks ( /t:Tracks) and sectors per track ( /n:Sectors) on the disk. It is preferred over the / t:Tracks and / n:Sectors parameters. Used for floppy disks to specify their size.
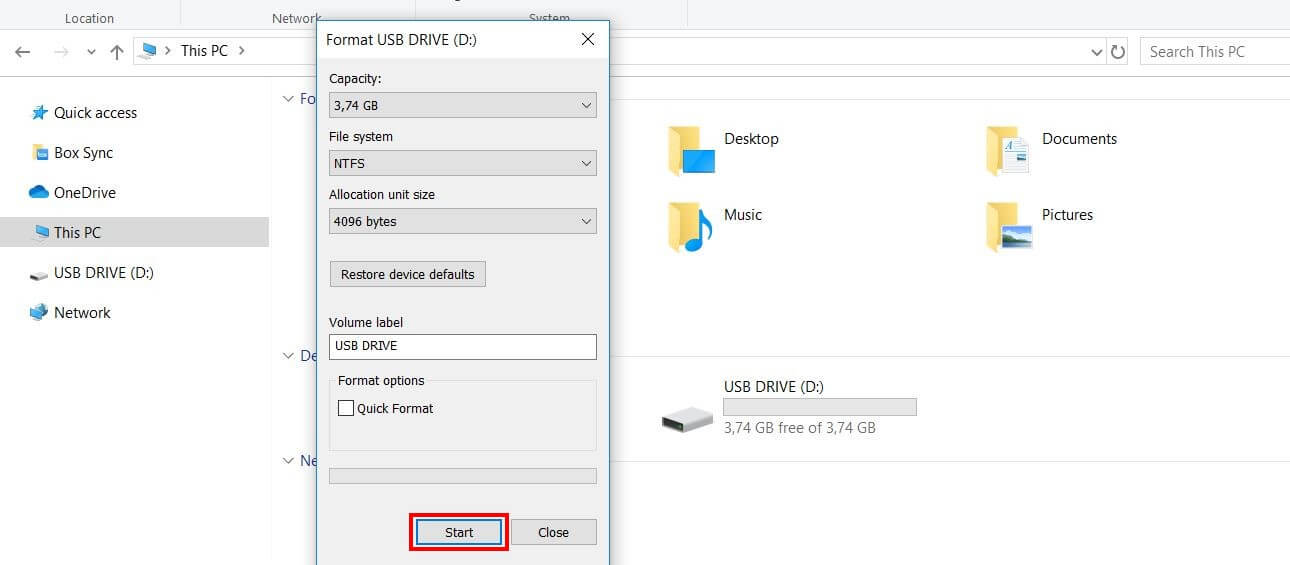
Used to dismount the mounted volume (if required) during the formatting process. It automatically compresses all files created on the new volume. Used to specify the allocation unit size for disk clusters. It causes the command to delete the existing root directory and file table and cuts the time required to format a disk when you are sure that it does not have any bad sectors. Used to perform a quick format of a previously formatted volume. If you do not use it, or if you use it without specifying the label, the Format command prompts you to specify a label once the formatting is complete. Used to assign a label to the formatted volume. When you are using this command for floppy disks, you can use only the FAT file system. This parameter supports the FAT, FAT32, and NTFS file systems. Specifies the file system to use for formatting. The drive letter is followed by a colon (:). Specifies the drive, volume, or mounted volume that you wish to format. Formatting a Disk or Partition with the Format Command The minimum and maximum partition sizes vary by the partition style chosen when the operating system was installed. The maximum file size can be up to 16 TB minus 16 KB. The maximum supported partition size ranges from 2 TB to 16 TB.
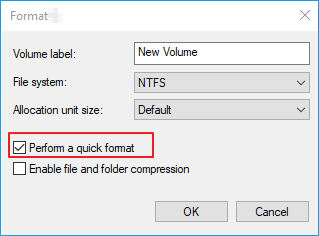
For more information check out Syngress Publishing's Winternals Defragmentation, Recovery, and Administration Field Guide, ISBN 1-59749-079-2).
You cannot use NTFS on floppy disks due to its limited capacity (Sysinternals has a utility for using NTFS on floppy disks. Other advanced features of NTFS include file and folder permissions, compression, encryption, and disk quotas. NTFS uses log file and checkpoint information to restore the consistency of the file system. Some of the features of NTFS include guaranteed volume consistency by means of transaction logging and recovery techniques. NTFS NTFS, which stands for New Technology File System, is an advanced file system that provides performance, security, reliability, and advanced features not found in FAT and FAT32 file systems. FAT32 file systems support a maximum partition size of 32 GB for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. The FAT32 file system supports smaller cluster sizes and larger volumes than the FAT file system, which results in more efficient space allocation. ▪įAT32 file system FAT32 stands for File Allocation Table32, an advanced version of the FAT file system. The maximum supported file size on hard disks is 2 GB. On floppy disks, this is limited by the capacity of the disk. This structure stores information about each file and directory so that it can be located later. It is a data structure Windows creates when a volume is formatted. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 support the following types of file systems: ▪įAT file system The File Allocation Table (FAT) file system is the original file system used by MS-DOS and other Windows operating systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
